Long-period and High-stability Three-dimensional Surfaceenhanced Raman Scattering Hotspot Matrix
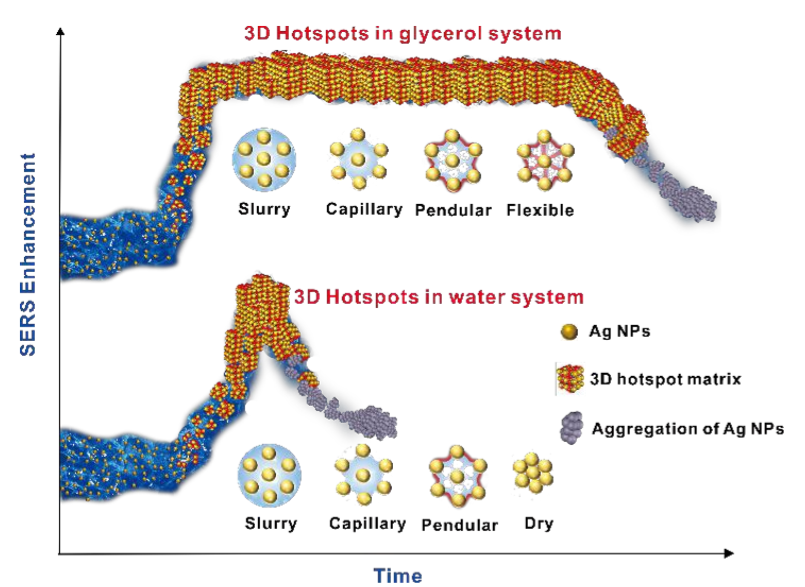
In recent years, our group developed a dynamic surfaced-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (D-SERS) strategy through solvent evaporation induced self-assemble of nanoparticles. The SERS measurement takes place during the evaporating process. According to the results from in situ synchrotron radiation small angle X-ray scattering (SR-SAXS) directly monitoring aggregation process and spatial distribution of sols, existence and controllability of hotspots have been confirmed. Moreover, compared with conventional 3D hotspot construction methods for SERS detection, the D-SERS is a very simple and flexible strategy. Firstly, SERS materials are extremely general and the substrate fabrication strategies are easy to implement. More importantly, during the process of collecting SERS spectra, the formed 3D hotspot matrix indicated the minimal polydispersity of particle size and maximal uniformity of interparticle distance. Thus, because of the presence of 3D ‘‘trapping well’’, the analytes has been trapped into 3D space, improving the high sensitivity. In addition, only a small amount of sample is needed and the mixed solution can be proceed on various solid films. Also, when another solvent drop is added to the dry substrate, this method can produce reversible SERS hot spots to trap molecules into inter-particle nanoparticles.However, despite all these advantages, there are still some problems in lengthening the range of the hotspots time in which it can increase the stability, repeatability and operability of D-SERS detection.
So in this study, a novel long-period and high-stability 3D hotspot matrix has been proposed by evaporating a drop liquid containing glycerol aqueous of Ag NPs and analytes. Ag NPs can self-close to form hotspot matrix driven by the solvent capillary forces. By conjunction of dark-field microscopy, in situ timedependent visible diffuse absorption spectra techniques, Raman spectra from these hotspots have been explored to indicate the evolution of an aqueous mixture during the evaporation process. The basis of these comprehensive data results showed that as compared to the D-SERS in water system with high sensitivity, the novel 3D hotspot matrix demonstrated significantly better signal stability, long period and reproducibility. Another advantage is that because of slow evaporation rate of glycerol, it can protect the nanoparticles and the analytes to be tested from photo-bleaching, photodesorption, photo-induced surface diffusion, substrate heating, or possibly changes in substrate morphology induced directly by the laser. Consequently, the long-period and high-stability 3D hotspot matrix has more practical applications outside pure scientific research, in fields such as scientific expeditions, crime scene analysis, medical diagnosis, and food safety and environmental testing.